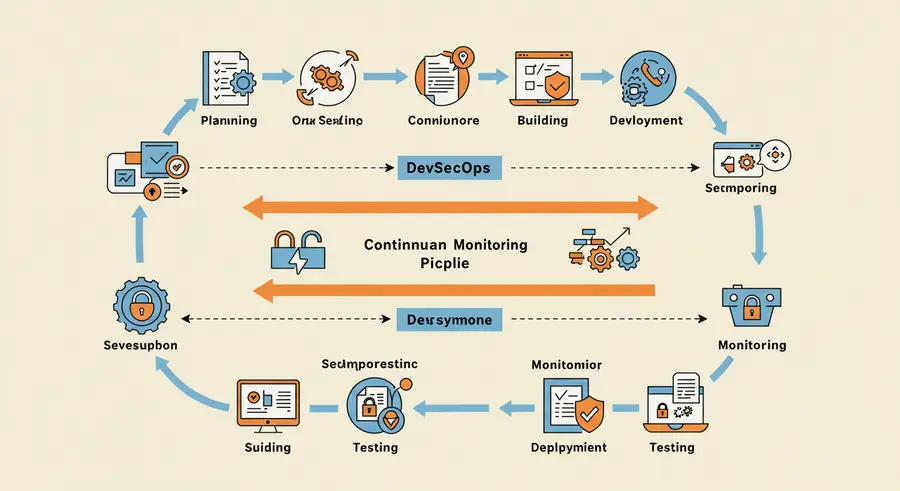
DevSecOps Continuous Monitoring: Vigilance Across the Lifecycle
Constant vigilance: The cornerstone of robust DevSecOps.
In the dynamic world of software development, simply building security into the initial stages of the pipeline is no longer enough. The threat landscape evolves rapidly, and applications, once deployed, continue to present new attack surfaces. This is where DevSecOps Continuous Monitoring becomes indispensable. It's the practice of maintaining constant vigilance over your applications and infrastructure throughout their operational lifespan, ensuring that security remains an ongoing, adaptive process rather than a static checkpoint.
What is Continuous Monitoring in DevSecOps?
Continuous monitoring in DevSecOps involves the systematic and automated collection, analysis, and reporting of security-related information. It extends beyond the build and deployment phases, encompassing runtime environments, user activity, configuration changes, and external threat intelligence. The goal is to proactively identify and respond to security threats, vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations in real-time or near real-time, minimizing the window of exposure and potential impact of breaches.
Key Aspects and Components
Implementing effective continuous monitoring requires a blend of technology, process, and people. Here are its core components:
- Log Management and SIEM: Centralized collection and analysis of logs from all layers of the application and infrastructure stack. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems correlate these logs to detect anomalous behavior and potential security incidents.
- Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP): RASP technologies are integrated directly into the application runtime environment, providing self-protection capabilities by analyzing application behavior and blocking attacks in real-time without human intervention.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Scanning: Continuously scanning your IaC definitions (e.g., Terraform, CloudFormation) for security misconfigurations and compliance violations before they are deployed.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Tools that continuously monitor cloud environments for misconfigurations, compliance deviations, and security risks, providing visibility and remediation recommendations.
- Vulnerability Management: Ongoing scanning of applications and infrastructure for known vulnerabilities, coupled with automated patching and remediation workflows.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Incorporating real-time threat intelligence feeds to inform monitoring systems about emerging threats, attack patterns, and indicators of compromise.
- Performance and Security Analytics: Leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning to identify subtle patterns that indicate security breaches or performance degradation due to security issues. For advanced insights and predictive analysis in complex data environments, tools offering AI-powered market insights can significantly enhance your monitoring capabilities, providing deep dives into security trends and anomalies.
Benefits of Continuous Monitoring
Adopting continuous monitoring brings a multitude of benefits to your DevSecOps practice:
- Early Threat Detection: Identify and respond to threats before they escalate into major incidents.
- Reduced Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR): Faster detection leads to quicker remediation and recovery from security incidents.
- Enhanced Compliance: Maintain continuous compliance with regulatory requirements by constantly monitoring configurations and activities.
- Improved Security Posture: Gain comprehensive visibility into your security landscape, allowing for proactive risk mitigation.
- Cost Savings: Prevent costly breaches and reduce the manual effort required for security audits.
- Better Collaboration: Fosters a culture of shared responsibility for security among Dev, Sec, and Ops teams.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
To successfully implement continuous monitoring, consider these strategies:
- Automate Everything Possible: From log collection to vulnerability scanning and alert generation, automation is key to scale and efficiency.
- Define Clear Metrics and KPIs: Establish what you will monitor, why, and what success looks like. Focus on metrics that provide actionable insights.
- Integrate with Existing Tools: Leverage your current CI/CD pipelines, observability platforms, and incident response systems.
- Establish Alerting and Response Playbooks: Ensure that when an anomaly is detected, there's a clear, automated, or semi-automated process for investigation and remediation.
- Regularly Review and Refine: The threat landscape is dynamic; your monitoring strategies should be too. Regularly review your tools, rules, and processes.
- Foster a Security-First Culture: Encourage all team members to think about security from the outset and understand their role in continuous monitoring.
Conclusion: A Non-Negotiable Pillar of DevSecOps
Continuous monitoring is not merely a feature of DevSecOps; it's a fundamental requirement for building secure, resilient, and compliant software in today's digital age. By embracing this proactive and pervasive approach to security, organizations can navigate the complexities of modern cyber threats with confidence, ensuring their applications and data remain protected throughout their entire lifecycle.
For more detailed information on specific security tools and their integration, explore resources like OWASP Top Ten and Google Cloud Security Command Center.